
You can now clone, pull and commit into your GitLab repositories, using Sourcetree.Name Description All-Projects Rights inherited by all other projects All-Users Individual user settings and preferences.

When cloning a new GitLab repo, you will have the initial option to specify a SSH key.Name is a unique name that you give to the local repositoryīefore you can push any changes to your GitLab repositories, you need to create a SSH key in Sourcetree and paste it into GitLab.Destination path is the folder on your machine, where you’d like to keep the local version of the repo.Enter the Source URL of the repository you want to clone (something like https: //…./somerepo.git).In Sourcetree, go to Window > Show Repository Browser.Further reading – clone a GitLab repository: You can now use your newly setup account to clone locally the GitLab repository you need. On Password, instead of entering your GitLab password, you need to enter the Personal Access Token that you just created. Now this is the most tricky (and confusing part).Click on Add… button to add your GitLab account.Back on Sourcetree, go to Preferences > Accounts.Click on Create personal access token button to complete the setup.
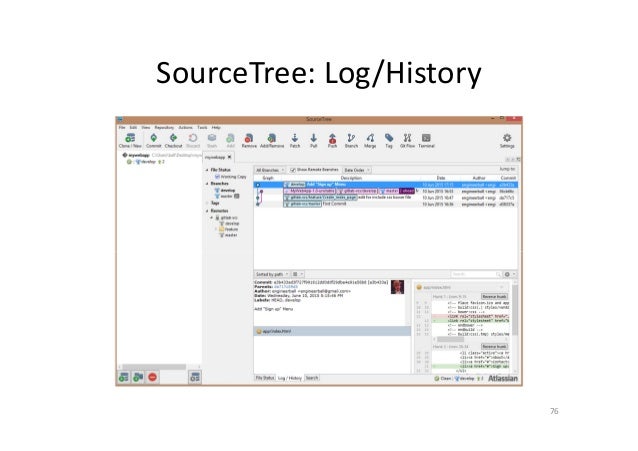
Create a new Token, using Add a personal access token, granting the access you want Sourcetree to have from Scopes.On your browser, open your GitLab account.A local installation of Sourcetree – version 4.0.2 (236), with embedded Git, version 2.27.0.
#Sourcetree gitlab windows


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
